interventricular septum thickness measurement|interventricular septum thickness end diastole : department Store The interventricular septum (IVS, or ventricular septum, or during development septum inferius) is the stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another.. The interventricular septum is directed . 3 de mai. de 2011 · New Edition / Discography (23 Releases) Жанр: R&B / Soul / Funk / New Jack Swing / Hip-Hop. Страна исполнителя (группы): USA. Год издания: 1982 .
{plog:ftitle_list}
L’affiliazione ai siti di scommesse mostra delle enormi prospettive da qui ai prossimi anni. Purché vi sia l’intenzione di sperimentare e imparare, il settore sa premiare anche chi ha poca o nessuna esperienza in materia. Il meccanismo è di agevole comprensione: l’operatore crea un link di affiliazione, da condividere poi sui propri canali di marketing, .
normal interventricular septum thickness
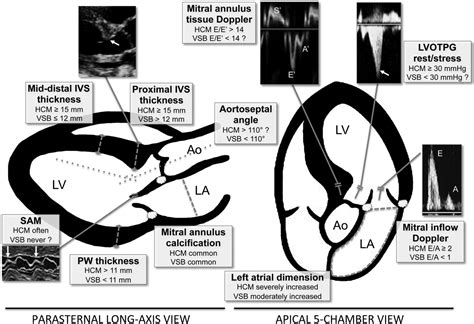
Normal septal thickness is 6 to 9 mm in women and 6 to 10 mm in men. The measurement should be made from the TG midpapillary short-axis view (midventricular IVS) and the ME long-axis view (basal IVS), at end diastole. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is characterized by left ventricular hypertrophy (wall thickness >12-15 mm; normal wall thickness is 12 mm or less, measured during diastole) .The interventricular septum (IVS, or ventricular septum, or during development septum inferius) is the stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another.. The interventricular septum is directed .
The interventricular septum, also known as the ventricular septum, refers to the triangular wall of cardiac tissue that separates the left and right ventricles (i.e., the lower chambers) of the heart. The entire .
measurements, height, weight, smoking habits, and lipid profile. We monitored 500 Air Force men with a . Interventricular septum thickness(cm) 0.89±0.12 0.93±0.11 <0.01
Two-dimensional echocardiography (2DE) is a widely used method to assess the thickness of the interventricular septum. Measurements of the interventricular septum are conventionally performed with M-mode echocardiography, and normal values for children have been reported [5, 6, 7, 10].M-mode echocardiography does not always give the most accurate .In this work, we address the problem of automated measurement of the interventricular septum thickness, one of the key parameters in cardiology, from B-mode echocardiograms. The problem is challenging due to high levels of noise, multi modal intensity, weak contrast. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the prognostic value of interventricular septum thickness (IVSd) on the incidence of cardiovascular diseases. Based on the general population in Northeast China, 10,349 participants were successfully followed up for echocardiography over a median follow-up time of 4.66 years, among which 4801 were .
The third window is the parasternal short-axis view, and the fourth is the apical four-chamber view. Measurements were corrected for body surface area (BSA). LVM was estimated as 1.05 {[left ventricular end-diastolic diameter (mm)+posterior wall thickness (mm)+intraventricular septum (mm)]3 _ [left ventricular end-diastolic diameter]3}/1000.
Technical errors in measurement, cutting the septum more obliquely on the parasternal long axis, may overestimate septal thickness. Concentric hypertrophy: symmetric LVH presents with similar measurements between septum, anterior and posterior free wall. . To measure LV outflow tract and intraventricular gradients, continuous Doppler is used .Septal and left ventricular posterior wall (LVPW) thicknesses and their ratios were studied at the left ventricular outflow tract and left ventricular cavity in 66 patients with echocardiographically diagnosed left ventricular concentric hypertrophy, 20 with idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis (IHSS), and 34 normal subjects. Concentric hypertrophy was due to hypertension in .
In this work, we address the problem of automated measurement of the interventricular septum thickness, one of the key parameters in cardiology, from B-mode echocardiograms. The problem is challenging due to high levels of noise, multi modal intensity, weak contrast due to near field haze, and non r .These measurements involve measuring the thickness of the interventricular septum (IVS) or the left ventricle anterior wall (LVAW), the left ventricular interior diameter (LVID) and the left ventricle posterior wall (LVPW). The software is designed to perform these measurements in the following order IVS/LVAW, LVID, LVPW. Once one Methods. This study was performed on 1,364 healthy adults aged 18–35 years.Standard trans-thoracic echocardiographic studies were performed to obtain end diastole measurements of left ventricular (LV) posterior wall thickness (PWd), interventricular septum thickness (IVSd), LV internal dimensions at end diastole (LVEDD) and end systole (LVESD), . A, Parasternal long-axis image at end diastole demonstrates linear echocardiographic measurements at the basal level of the LV: interventricular septum diameter (1), LV end-diastolic diameter (2), and posterior wall thickness (3). B, Midventricular parasternal short-axis image demonstrates LV wall thickness measurements.
Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM) is a relatively common disorder. Historically, it has been referred to as idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis. HOCM is a significant cause of sudden cardiac death in young people, including well-trained athletes, affecting men and women equally across all races. In most patients, it results from asymmetric . The LV mass was calculated from linear measurements obtained from parasternal views. Assessment of right ventricular . The interventricular septum thickness (white arrow), the left ventricle end-diastolic diameter (red arrow) and the posterior wall (PW; yellow arrow) thickness are measured just distal to the mitral leaflets tips .
interventricular septum vs sulcus
Interventricular septum thickness in end-diastole (IVSd) is one of the key parameters in cardiology. This paper presents a fast algorithm, suitable for pocket-sized ultrasound devices, for measurement of IVSd using 2D B-mode parasternal long axis images. The algorithm is based on a deformable model . Example of interventricular septal thickness measurement obtained by M-mode echocardiography in the diastole. Figure 3. Receiver operating curve for interventricular septal thickness as a novel macrosomia . The first and most commonly used echocardiography method of LVM estimation is the linear method, which uses end-diastolic linear measurements of the interventricular septum (IVSd), LV inferolateral wall thickness, and LV internal diameter derived from 2D-guided M-mode or direct 2D echocardiography. The ultrasonographic measurements of fetal epicardial fat pad thickness and fetal cardiac interventricular septal thickness were statistically significantly higher in GDM pregnancies (p value < 0.0001) as compared to the controls. Thus, these two parameters can serve as excellent ultrasonographic markers in the prediction of GDM.
Conclusion The ultrasonographic measurements of fetal epicardial fat pad thickness and fetal cardiac interventricular septal thickness were statistically significantly higher in GDM pregnancies .
Initial M-mode standard recommended inclusion of the edges as part of interventricular septum thickness, but exclusion of the posterior wall epicardial edge . Investigators of the University of Pennsylvania developed a criteria (The Penn Convention) in which all edges are not included in parietal thickness measurements, but are considered as . A sigmoid-shaped interventricular septum (SIS) is generally considered a normal part of the aging process and is of little clinical significance. . Basal-septal hypertrophy may also occur in a subset of older normal subjects, with normal wall thickness (WT) elsewhere, and is considered to be an age-related anatomic variant. . BP measurement . 1. Left ventricular wall thickness. Both the interventricular septum and LV free wall should be assessed, with measurements made on 2-dimensional echocardiography, on right parasternal views at end-diastole (the frame prior to closure . Cardiac ultrasound utilizes transthoracic or transesophageal positioning of the transducer to measure the left ventricular end-diastolic diameter, posterior wall thickness, and interventricular septum thickness. From these measurements and the patient’s height and weight, the LV mass index can be determined.
Part 1 (n=92). IVSd diastolic interventricular septum, LVEDd left ventricular end-diastolic diameter, LVPWd diastolic left ventricular posterior wall thickness, LVMI left ventricular mass index, Mean diff, mean difference, CI confidence interval, LoA limits of agreement, SDC smallest detectable change, LVH WT was defined as a Z-score of IVSd and\or LVPWd > + 2 (according . Conclusion The ultrasonographic measurements of fetal epicardial fat pad thickness and fetal cardiac interventricular septal thickness were statistically significantly higher in GDM pregnancies .
Download scientific diagram | (a) Example measurements of the interventricular septum thickness (IVSd), left ventricular internal dimension (LVIDd) and left ventricular posterior wall (LVPWd .
WEBThis guide explains how to use variables and do basic programming in Twine 2.1. All these instructions are based on the SugarCube 2 story format. Before beginning, make sure that your Twine 2.1 game is set up for the SugarCube 2 format. To do so, click on the name of your story in its main “story map” view.
interventricular septum thickness measurement|interventricular septum thickness end diastole